Featured
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Calculating Local Anesthetic Dosage
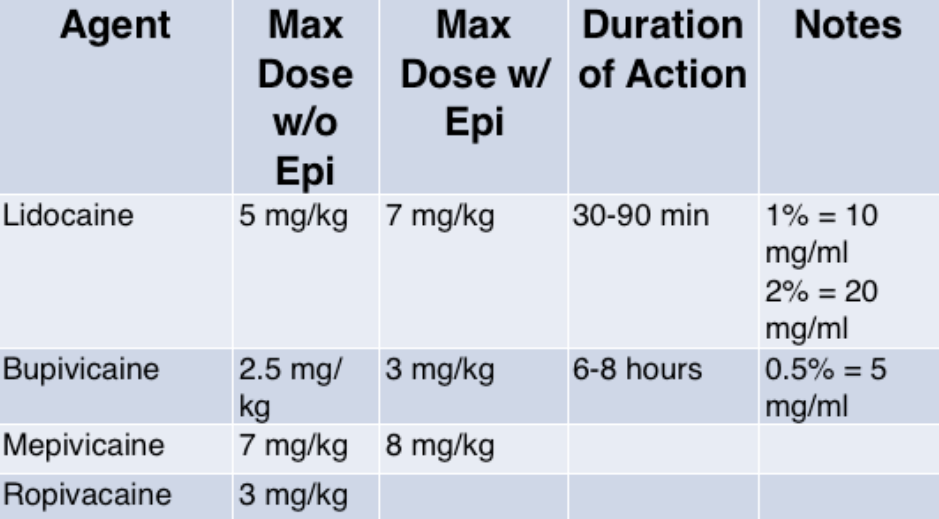
Calculating Local Anesthetic Dosage. Examples.5% solution =5 mg/ml= 3 x 1 mg= 5 2% solution= 20 mg/ml=20 2 ml. A 1% solution of lidocaine has 1g/100 ml = 1,000 mg/100 ml = 10 mg/ml;
N another consideration when you get into needing high amounts of local anesthesia is to not place it all in a short period. While there likely is a higher safe dose when epinephrine is added, we no longer include that estimate on this calculator, and as always,. Two equal doses of the same anesthetic agent can produce markedly different responses in two different patients.
Local Anesthetic Systemic Toxicity (Last) Is A Rare But Avoidable Consequence Of Local Anesthetic Overdose.
A 1% solution of lidocaine has 1g/100 ml = 1,000 mg/100 ml = 10 mg/ml; (most toxic drug) is applied when calculating total drug doses. N holds 1mg in 10ml.
To Assess Whether The Features Of The App Warrant Spending Nearly $10 For It;
Previous versions of goldfrank’s reported an increased maximum allowable dosage due to the vasoconstrictive effects of epinephrine when added to local anesthetics. Food and drug administration (fda) regularly updates maximum recommended dosages (mrds) for local anesthetic drugs. Although the fda has provided mrds for local anesthetic drugs (table 1), patient response to drug dosage cannot always be predicted.
4) 1:1,00,000 Concentration Means 1 Part Of Adrenaline.
Since we want to be safe, before injecting / infiltrating the local anesthetic, it is good practice to calculate the safe “upper limit” dose. To review the applicability of the local anesthesia app for guiding safe maximum dosing of local anesthetic; This article will review the mechanism of action of local anesthetic toxicity.
In Canada, The Recommendations For Bupivacaine Are 0.9 Mg/Lb And 2.0 Mg/Kg.
A cadaver head at a local anesthetic ce course. Calculating local anesthetic drug doses 2 cartridges 2% lidocaine admin 100 lb pt. We compared the performance of the nomogram with a spreadsheet and a general.
Unlike Local Anesthetic Agent, The Dose Does Not Depend On The Patient's Body Weight.
Epidural solutions of local anesthetics and opioids, such as bupivacaine and fentanyl, are commonly employed for intraoperative use, labor and delivery, and postoperative analgesia. True % solution then # mg/ml delivered= total mg dose. Body weight versus spinal length.
Popular Posts
Mean Of Binomial Distribution Calculator
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Comments
Post a Comment